STM: Small and Powerful RS485 Transceiver

The STR485 is a small and powerful RS485 transceiver with a dual data rate and compatibility with 1.8 V power supplies to significantly simplify designs. It also includes many fail-safe features to protect data from interferences and increase the safety of the entire system. No matter how smart a factory or an industrial complex is, the smallest components can cause massive delays and serious malfunctions, bringing the whole structure down. For instance, the RS485 communication standard is a critical system in an industrial setting because companies use it for controlling motors, development, debugging operations, or merely interconnecting a large number of machines to ensure they communicate with one another. It’s easy to see why choosing the right transceiver is crucial and that despite its deceptively small package, it can be the root cause of hugely crippling and expensive issues.
RS485 remains a highly popular serial communication standard in the realm of the smart industry. Thanks to its multipoint topology, it can connect more than two terminals, unlike its predecessor, the RS232 protocol. A typical RS485 transceiver can drive up to 32 devices, and there can be up to 256 transceivers on the same bus, opening the door to a massive and complex structure. In low data rate mode, which offers more bandwidth than RS232’s highest speed, connections can reach as far as 1200 meters. Finally, because RS485 uses twisted pair cables, it more appropriately fends off magnetic fields compared to the straight cables of other standards. All these advantages contribute to the popularity of RS485, and it was fundamental to offer a component that was both flexible and robust.
The Flexibility of ST’s RS485 Transceiver: Low Voltage and Data Rate Selection
The STR485’s compatibility with 1.8 V power supplies is a direct response to new design challenges that aim for a simplification of the PCB in low power systems. RS485 is ubiquitous, which means that it connects an increasing number of small devices, such as simple networking equipment. These products use low-voltage processors and have tight power consumptions. Thanks to its compatibility with 1.8 V power supplies, the STR485 doesn’t require a voltage adapter when designers use it in low power environments since they can drive the RS485 transceiver with the processor, for instance. Engineers working on a more traditional system will appreciate that the component also accepts 3.3 V power supplies, which means that they can qualify a single part for a broader range of systems to simplify their operations.
Another testament to the flexibility of the RS485 is its dual data rate. If engineers connect the SLR (slew rate) pin of the STR485 to the ground, they will enjoy a 20 Mbps throughput. On the other hand, if they connect it to the VL power supply, the data rate will drop to 250 kbps, but it will enable data transmission over much longer distances. It is important to know that if designers leave the pin floating, the system will default to a 20 Mbps data rate thanks to the presence of an internal pull-down, but we strongly discourage such practices to avoid any potential issue with the microcontroller and instead invite engineers to connect the SLR pin to the ground or the logic supply voltage.
The Robustness of ST’s RS485 Transceiver: ESD Protection and Fail Safe Termination
To protect devices against electrostatic discharge (ESD) the STR485 offers internal protection on the driver’s output and receiver’s input. The limits are high since we protect up to ±4 kV according to the human body model (HBM), which simulates a discharge if a human were to touch it, as well as a limit of up to ±8 kV contact discharge and ±16 kV air discharge. These numbers are possible thanks to the integration of new protection measures on the die, and it enables a high degree of resiliency. EDS is often a severe problem in manufacturing, or industrial settings and RS485 transceivers are especially susceptible to it. This new measure also explains why our component is compliant with the IEC61000-4-4 standard protecting against fast transient bursts.
The STR485 also includes various features to protect the system from potential harm or malfunctions. For instance, a thermal shutdown circuit turns the driver outputs off when the junction temperature reaches 165 ºC. There’s also a fail-safe system when the receiver is open, shorted, or idle. The RS485 standard establishes that the on state is characterized by a differential input voltage of +200 mV whereas the off state requires -200 mV. However, the protocol doesn’t specify a particular behavior when the differential input is between these two measurements, meaning that the receiver is open. Hence, our fail-safe system disables the receiver when it is open, shorted, or idle (no active driver), to ensure stability and prevent any undefined state that could potentially lead to failures.
Small and Powerful
A key partner in the telecom industry is currently looking into the STR485, and its feedback is incredibly positive. Furthermore, because we made our transceiver pin-to-pin compatible with competing models, engineers can swap their old part for our component and enjoy the reliability that comes from the STR485, our manufacturing lines, and customer support.
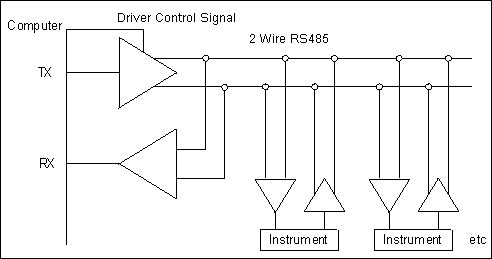
What does Half Duplex mean?
Half Duplex means that data can only pass in one direction at a time. In this arrangement, both TX and RX signals share a single pair of wires. This can save in installation costs and make the system less complex in the physical dimension