All about LoRaWAN – Everything you need to know

The story of LoRaWAN begins in 2009 when 2 friends Nicolas Sori and Olivier Seller from France, targeted to develop a long-range, low-power consumption, modulation technology. In 2010 François Sforza joined and a company called Cycleo was incorporated. The company aimed at using these low-range frequencies to add wireless capabilities for gas, water, electricity meters etc.
In 2012 Semtech Corporation, a California-based company acquired Cycleo. Semtech Corporation recognized the potential of Cycleo’s SCDMA technology and acquired the company to integrate its technology into Semtech’s existing product portfolio, including the LoRa technology that Semtech had already been developing.
LoRaWAN stands for Long Range Wide Area Network, and it’s a wireless communication technology designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) devices and M2M applications. It provides, Long Range, Low Power, Low Bandwidth and Low Data Rate.
It allows various devices to communicate over long distances with a central network, using various low-frequency bands.
The frequencies chosen are different in different regions of the world.
Some of the most commonly used frequency bands for LoRaWAN include:
- 868 MHz band: This frequency band is used in Europe, and it allows for a maximum output power of 14 dBm.
- 915 MHz band: This frequency band is used in North America, and it allows for a maximum output power of 30 dBm.
- 923 MHz band: This frequency band is used in Asia and Australia, and it allows for a maximum output power of 14 dBm.
These frequencies are typically not used by other technologies like WiFi and Bluetooth, thus reducing interference.
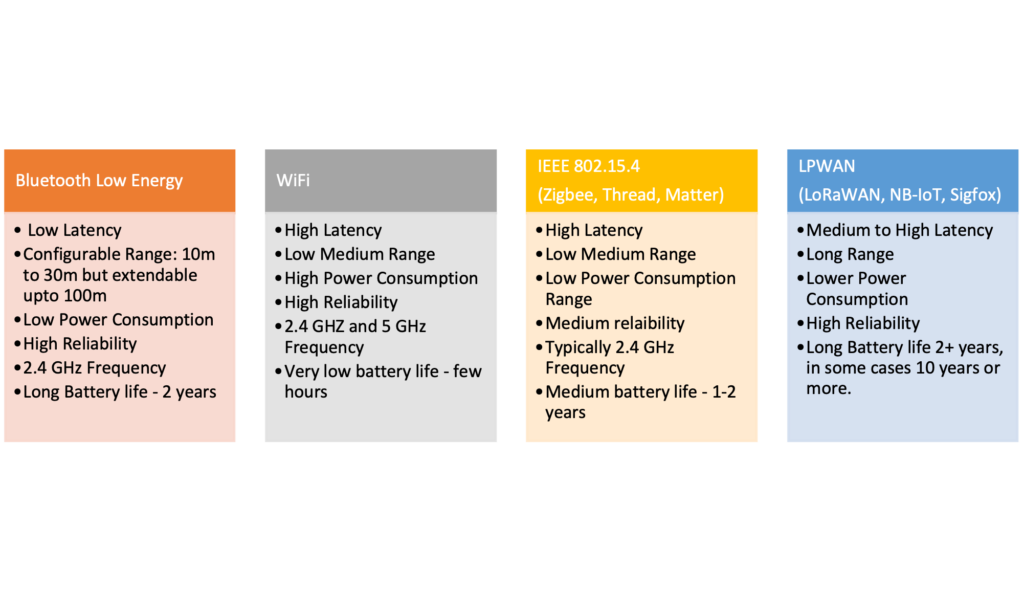
When we talk about Internet of things or m2m communication, we have various options available for communication
- Wired: Ethernet, PLC (Powerline Communication), RS485, RS232, CAN Bus, MODBUS etc.
- Wireless
- High Frequency/Higher Power Consumption/ Lesser Range: WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Cellular, RFID, NFC, etc.
- Low Frequency/ Lower Power Consumption/Higher Range: LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NBIoT
Note: Above classification is fuzzy and there are further classifications and differences between each communication option.
LoRaWAN Network Fundamentals
To fully understand LoRaWAN networks, we will start with a look at the technology stack. As shown below, LoRa is the physical (PHY) layer, i.e., the wireless modulation used to create the long-range communication link. LoRaWAN is an open networking protocol that delivers secure bi-directional communication, mobility, and localization services standardized and maintained by the LoRa Alliance
LoRaWAN Network
End Devices: Usually sensors or actuators. They are the source or destination of data – like temperature, human presence, humidity, ambient, sulphur content, air quality etc . A source in case of sensors and a destination in the case of actuators – like LEDs, Buzzer/Siren, Speakers, valves, Motors etc. They are also called nodes
Gateways: They receive LoRa-modulated RF messages from end devices or nodes, and forward these messages to the LoRaWAN end server or cloud. They make use of other wired and wireless technologies like WiFi, Cellular services, Ethernet etc. to connect to a cloud server and transfer data. They can be smart or dumb gateways based on intelligence and data processing capabilities. The use of smarter gateways is part of Edge computing architecture.
Network Server: They manage the entire LoRaWAN network and help adapt the system to the ever-changing conditions of the network. They help streamline the cloud connectivity process, as well as manage traffic and end-to-end encryption of the network. They help ensure the authenticity of every sensor node and the integrity of the messages exchanged.
Application Servers: They are responsible for handling the data and massaging, splicing, and reorganising, according to the requirement of the application. This stage ensures that the heterogeneous data is aggregated and organized so that the users of the system can extract relevant data
Find more in-depth information Here
How can one learn about LoRaWAN to develop practical solutions
There is a large difference when it comes to learning about any technology and being able to develop a solution. To start learning about LoRaWAN and begin a journey to develop solutions using LoRaWAN you have to:
- Understand the Basics: Learn about fundamentals, basic concepts, terminologies used in LoRaWAN networks
- Study the technology: Learn and understand the stack, along with each layer in depth.
- Explore Use Case: Exploring possible utility areas and existing use cases helps understand a technology better. As a solution developer it helps in exploring ideas, and solving problems easily and efficiently.
- Get Hands-on experience: There are development kits and sensor modules based on LoRaWAN technology. There are also many open-source applications and servers that developers can use to rapidly learn and develop a prototype
LoRa Development Kits
- The Things Industries’ The Things Uno and The Things Node https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/docs/devices/uno/
- STMicroelectronics’ STM32 Discovery kit IoT node: https://www.st.com/en/evaluation-tools/b-l072z-lrwan1.html
- MultiTech MultiConnect Conduit : https://www.multitech.com/brands/multiconnect-conduit
- SX1261/SX1262 Development Kit: https://www.mouser.in/new/semtech/semtech-sx1261-sx1262-dev-kits
Courses from Semtech: https://lora-developers.semtech.com/
LoRaWAN Alliance
With more than 500 member companies, the LoRa Alliance is one of the fastest-growing technology alliances. A community of innovators, the LoRa Alliance is committed to standardizing low power wide area networks (LPWANs). To this end, the group provides the LoRaWAN Specification (https://lora-alliance.org/search/specification) free of charge. The specification is based on open standards and provides for certified interoperability.
The LoRa Alliance also offers the LoRaWAN Certification Test Tool, to help manufacturers ensure that their devices are fully LoRaWAN-compatible prior to sending those devices to an Authorized Test House for formal LoRaWAN Certification testing.
For more information on the LoRa Alliance, visit their website: https://lora-alliance.org
Applications of LoRaWAN Technology
- Smart Agriculture – sensors to detect soil moisture, temperature, humidity, UV levels, ambient lights, wind speeds etc of the area and control various systems. Can also be used in large greenhouses
- Smart Cities: Smart parking, smart lighting, waste management, air quality monitoring etc.
- Industrial Automation: LoRaWAN can be used to monitor various performance metrics of machines and processes, create a digital twin of the factory, and various safety gadgets etc
- Asset Tracking: Local and Global level asset tracking
- Healthcare: Various body sensors can be used for the health tracking of patients
- Environmental Monitoring: Air Quality, UV, Ambient Light, Water quality etc.
- Home Automation: Smart energy meters, smart water meters, smart heaters, smart lights etc.
Author: Hrishikesh Kamat is an experienced IoT professional and a renowned author on IoTAdda. He is also the CEO of Shalaka Connected Devices, an IoT Design House and Consultancy Company based in Pune, India. With expertise in IoT technologies, Hrishikesh shares valuable insights on topics such as connected devices, data analytics, and IoT applications. Their articles are known for simplifying complex concepts and providing practical advice. As an active participant in IoT communities, Hrishikesh stays at the forefront of the industry and explores emerging technologies. With Hrishikesh Kamat as an author, readers can expect engaging and informative articles that inspire innovation in the world of IoT.